Cummins introduced the 6BT in 1984, and they designed it for use in agricultural equipment. In 1989 Dodge teamed up with Cummins to offer the 5.9L Cummins in their heavy-duty pickup trucks.
The Cummins-powered Ram quickly became a popular alternative to the large gasoline engines typically found in heavy-duty pickups. Ever since then, diesel pickup trucks have grown into a massive market in the US.
Diesel engines are far better for heavy towing than gasoline engines, which is part of the reason for their enormous success in the US truck market.
In this short article, we are going to cover everything from engine specifications to real-world applications and increasing power output.
History of the 6BT Cummins
The 6BT Cummins is part of the B Series engines that Cummins Inc. began producing in 1984. Although the series included a range of engines with different numbers of cylinders and displacement, it was the 6BT, a 5.9-liter inline-six engine, that stole the spotlight.
Initially, the 6BT was developed for agricultural, industrial, and commercial applications. However, it was Dodge that introduced this powerhouse to the light-duty truck market in 1989, under the hood of its Dodge Ram.
he partnership with Dodge propelled the 6BT to popularity, giving it a legendary status among diesel truck enthusiasts. It was this partnership that continued until 1998 when it was replaced by a 24-valve variant, the ISB 5.9L.
6BT Cummins: Engine Basics
The 6BT Cummins is a 5.9L inline-6, with an OHV design and 12 valves; Another name for the 6BT is “12-Valve.” The architect of the 6BT is roughly similar to the AMC inline-6 of the time.
The 6BT has an iron cylinder block as well as an iron cylinder head. While this makes it extremely heavy, it also makes it extremely strong. Strength is one of the 6BT’s most known features.
Many people have pushed them past 1,400 horsepower, and the stock ones can exceed 1,000,000 miles if properly cared for.
One of the best features of the 6BT Cummins is its entirely mechanical fuel system, which makes it excellent for an engine swap because there is only a couple of wires to make the engine run.
But, because of this, you can’t just plug a tuner into it and produce more horsepower. You can view this mechanical fuel system as either a pro or as a con.
The simple mechanical fuel injection system is unlikely ever to fail, but you cannot tune it by using a small handheld tuning device.
- Production Years: 1989 – 1998
- Configuration: Inline 6-Cylinder
- Displacement: 5.9L – 359ci
- Cylinder Head Material: Cast Iron
- Cylinder Block Material: Cast Iron
- Valvetrain: OHV – Two valves per cylinder
- Deck: Closed Deck
- Bore: 102mm
- Stroke: 120mm
- Injection Pump: Bosch VE44 (1989 – 1993) – Bosch P7100 (1994 – 1998)
- Horsepower: 160 – 215 hp
- Torque: 400 – 440 lb-ft
6BT Cummins: Real-World Applications
The 6BT was the first in the Cummins “B” engine family to be used in a light truck. However, it was initially designed for use in Case agricultural equipment.
Dodge struck up a deal with Cummins in 1989 to use the 6BT in their 3/4-ton and 1-ton trucks.
- Agricultural equipment
- Dodge Ram 3/4 Ton
- Dodge Ram 1 Ton
Later down the line, Cummins introduced the 24-valve QSB (Quantum System B) engine. The QSB engine was used in marine, agricultural, and construction equipment.
6BT Cummins: Performance Data
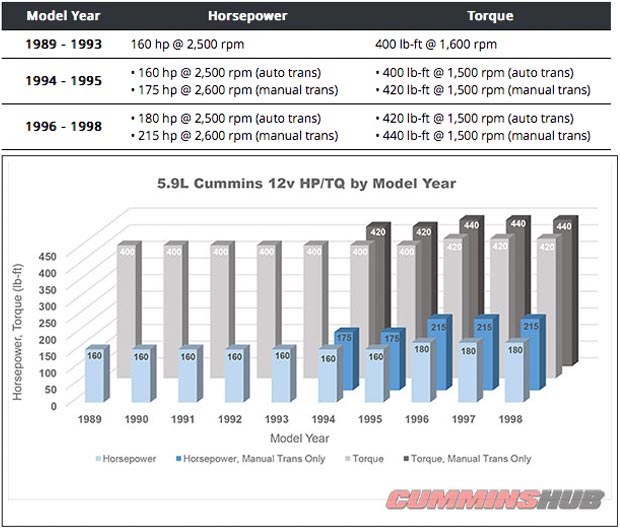
When the 6BT was first used in the Dodge Ram in 1989, it produced 160 hp @ 2,500 rpm and 400 lb-ft @ 1,600.
While horsepower was down from the traditional gasoline engine, torque was up by quite a decent amount. In the world of trucks, torque is the number that matters.
In 1994 horsepower for the manual transmission models was increased to 175 horsepower, and torque to 420 lb-ft.
Then in 1996, the power was increased to 180 horsepower and 420 lb-ft for automatic transmission models. Power for manual transmission models was increased to 215 horsepower and 440 lb-ft of torque.
We wouldn’t have this horsepower/torque chart without CumminsHub, so be sure to check them out!
Durability and Performance
One of the reasons why the 6BT Cummins has remained popular among diesel enthusiasts is its durability. The engine was designed to last, and many 6BTs are known to have covered a million miles or more before requiring any serious engine work.
The cast-iron construction and robust mechanical fuel system contribute significantly to this durability.
Performance-wise, the 6BT was an improvement over its competition when introduced. Despite the raw figures not sounding overly impressive by today’s standards, it offered power, reliability, and fuel economy that was second to none in its era.
This engine also has a huge aftermarket following, which means there are lots of options for those wanting to increase power and performance. Plain and simple, it’s one of the most reliable AND most modified diesel engines of all time.
6BT Cummins: Tuning Potential
If factory specifications bore you to death as they do to me, then you’ll enjoy this next section. Who cares what the 6BT Cummins was like from the factory? What is it capable of with some aftermarket help?
Well, the 6BT’s bottom end is good for about 800 horsepower and 1400+ lb-ft. Anything past that, and you’ll need a built bottom end. The transmission will either need a beefy clutch for the manual or an entire transmission build for the automatic.
How can you easily get power out of your 6BT Cummins? Since it has an entirely mechanical fuel system, getting power out of it requires turning up the fuel, which is typically done by grinding down the fuel plate or purchasing a performance fuel plate.
The fuel plate controls the flow of diesel to the engine per a given RPM. Bigger fuel injectors are also very important for the 6BT Cummins. Naturally, the standard upgrades like a larger exhaust also help the 6BT gain power.
RELATED: 4BT Cummins: Everything You Want to Know
The folks over at Hot Rod Garage were able to get 320 horsepower, and 800 lb-ft out of their 6BT swapped 1973 Dodge Ram.
They did this by installing a larger turbocharger, larger injectors, a performance fuel plate, and a larger exhaust. With those modifications, they doubled the horsepower and torque.
What they did with some simple changes shows just how great the 6BT is for modifications. Newer diesel engines, such as the 6.7L Cummins, make even more power than a modified 6BT with an ECU tune and simple emissions delete mods.
6BT Cummins: Common Problems
The 6BT is a reliable engine thanks to its fully mechanical fuel system, simple wiring, and overall straightforward design.
Like an engine, however, it does have some fatal flaws. Two major problems are common for the 6BT Cummins: the “53” block and the “killer dowel pin,” both of which can result in a dead engine.
The “53” block problem occurred in certain 24v ISB engines from 1999 to 2002; around 100,000 engines were stamped with the number 53.
These “53” blocks were produced by a Brazilian company that did not use the correct chemical mixture required by Cummins. This weak chemical mixture results in the block cracking, which will cause coolant leaking and engine overheating.
A cracked cylinder block is pretty much unfixable and should be avoided.
The “killer dowel pin” can be found across all 6BT engines and even 4BT engines. The dowel pin is located in the timing gear case and over long periods of time, it will begin to wiggle loose from its dowel hole and eventually fall out.
When it falls out it will either get caught in all the timing gears which can stop the valves and cause valve/piston contact, ruining the engine or, it will simply fall into the oil pan.
Another possibility is the dowel pin hitting a timing gear and shooting out the crankcase, causing terminal damage. If you haven’t already, order a “killer dowel pin” fix kit, which solves this issue before it kills your engine.
Summary
So overall, the 6BT Cummins is an excellent engine. It was the engine that genuinely made diesel pickups popular in America.
The entirely mechanical fuel system makes it great for engine swaps and also makes it extremely reliable.
Getting power out of it is as simple as turning up the fuel and bolting on a better turbocharger. You can find even more 6BT information on Wikipedia.
The 6BT Cummins is not in production for road-going vehicles today, but it has left a lasting legacy. Many engines still run in older Dodge Rams, and the engine is a popular choice for engine swaps due to its power, reliability, and the availability of aftermarket support.
Moreover, Cummins continues to manufacture the 6BT for industrial, commercial, and agricultural applications where its ruggedness and reliability make it a preferred choice.
The 6BT Cummins is more than just a diesel engine. It has earned a legendary status in the world of diesel engines for its power, reliability, and ruggedness. The engine might not be in production for the road-going vehicles today, but it still holds a strong presence in many sectors and among car enthusiasts.
It really is a testament to the engineering prowess of Cummins Inc. and remains one of the most influential engines in the history of diesel-powered vehicles. Quite frankly, it’s one of the best engines ever regardless of fuel type.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases made through links on this website.

Great story,
I have 97 BT 6 and want to put into my 1993 2500 4×4 Suburban,
This story just reinforced my reasons for the swap, big power and towing torque,
Can’t wait to get started,
Now there are a ton of after market parts, motor mounts, tranny upgrades,
If there is anything you could point out, or website to look at I would greatly appreciate it,
Troy Powers @ machineandfab@gmail.com
Has any one fitted either 4 or 6 cylinder Cummins to International D1310
What is the weight of these engines
1989 5.9 built fresh, going in a 1967Ford Highboy
torc pounds per ft on adjusting bolt on tappets
5.9, 6bt
yes………………………………………..
I have faced some problem you described in above and still prefer this 6BT cummins